
Regenerative Agriculture: A Holistic Farming Approach to Tackle Climate Change
Climate change is one of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time, and agriculture is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions.
According to the United Nations, agriculture is responsible for 14% of global greenhouse gas emissions, with livestock production accounting for a significant portion of that.
There is growing interest in regenerative agriculture as a solution to climate change. Regenerative agriculture is a holistic farming approach that emphasizes soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem restoration. In this article, we'll explore the principles of regenerative agriculture, its potential benefits for the environment and local communities, and discuss some of the challenges and opportunities facing the movement.
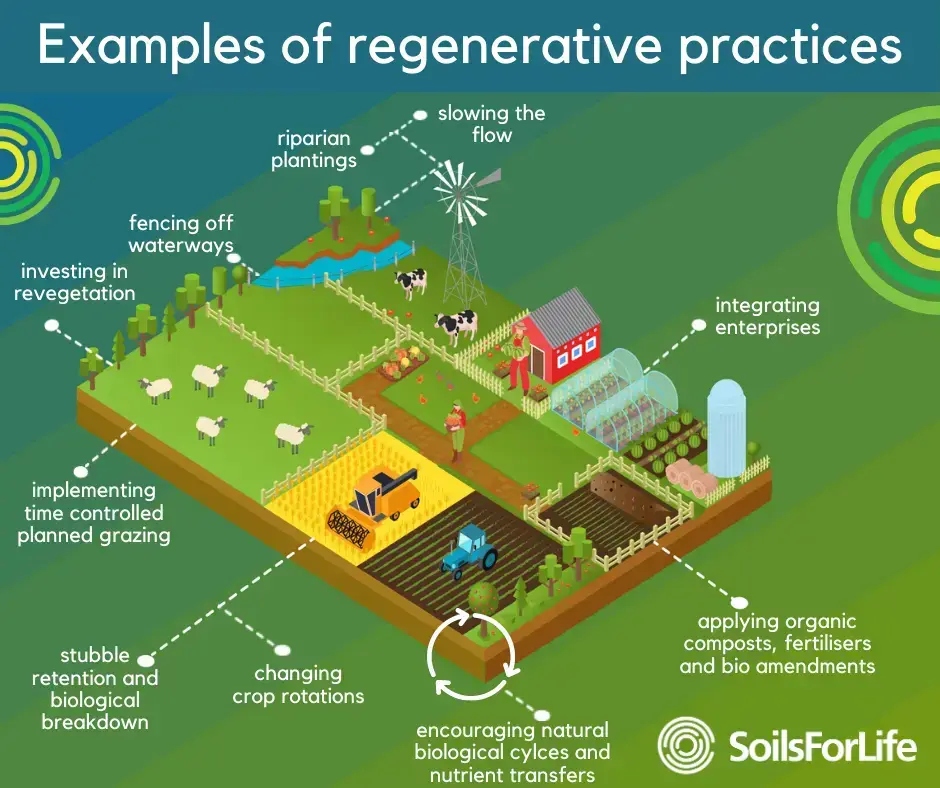
Principles of Regenerative Agriculture
Regenerative agriculture is based on a set of principles that prioritize soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem restoration. Some of the key principles of regenerative agriculture include:
-
Soil health: Regenerative agriculture focuses on building healthy soil, which is critical for the growth of healthy plants and the sequestration of carbon. This involves practices like cover cropping, crop rotation, reduced tillage, and the use of compost and other organic matter to improve soil fertility and structure.
-
Biodiversity: Regenerative agriculture aims to promote biodiversity by planting a variety of crops and using crop rotations to prevent soil depletion and disease. It also encourages the use of natural pest management techniques, such as beneficial insects, to reduce the need for pesticides.
-
Ecosystem restoration: Regenerative agriculture seeks to restore natural ecosystems by incorporating practices like agroforestry, which involves planting trees and shrubs alongside crops, and the use of hedgerows to provide habitat for pollinators and other beneficial species.
Potential Benefits of Regenerative Agriculture
Regenerative agriculture has the potential to deliver a range of benefits for the environment, local communities, and the global food system. Some of the potential benefits of regenerative agriculture include:
-
Carbon sequestration: Regenerative agriculture practices can help sequester carbon in the soil, which can help mitigate climate change. According to a recent study, regenerative agriculture practices could sequester up to 5.5 billion metric tons of CO2 per year, equivalent to removing 1.2 billion cars from the road.
-
Improved soil health: Regenerative agriculture practices can improve soil health, which can lead to higher crop yields, reduced erosion, and better water retention. Healthy soil can also help reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which can have negative impacts on the environment and human health.
-
Biodiversity conservation: Regenerative agriculture practices can help promote biodiversity by providing habitat for a variety of species, including pollinators and other beneficial insects. This can help support ecosystem resilience and improve the overall health of natural systems.
-
Local economic benefits: Regenerative agriculture can support local economies by promoting sustainable farming practices, creating jobs in the food system, and increasing the availability of locally-grown food.
Challenges and Opportunities
While regenerative agriculture holds tremendous promise for the future, there are also significant challenges and opportunities facing the movement. Some of the key challenges include:
-
Scaling up: Regenerative agriculture is still a relatively small movement, and there are challenges associated with scaling up these practices to the level needed to make a significant impact on climate change.
-
Policy support: Regenerative agriculture faces a lack of policy support and funding, which can make it difficult for farmers to transition to these practices.
-
Knowledge and education: Many farmers lack the knowledge and education needed to transition to regenerative agriculture practices, and there is a need for more training and support to help them make the transition.
-
Market access: Regenerative agriculture products can be more expensive than conventionally-grown products, and there is a need for more market access and support to help farmers and consumers make the switch to these products.
Despite these challenges, there are also significant opportunities for the growth and development of regenerative agriculture. Some of the key opportunities are as follow:
-
Consumer demand: There is growing consumer demand for sustainably-grown and locally-sourced food, which could help drive demand for regenerative agriculture products.
-
Public awareness: Regenerative agriculture is gaining more attention in the media and public discourse, which could help raise awareness and support for these practices.
-
Private sector engagement: Private companies, such as food retailers and manufacturers, are starting to show interest in regenerative agriculture and are exploring ways to incorporate these practices into their supply chains.
-
Climate policy: Regenerative agriculture could be an important part of climate policy solutions, and there is increasing interest in incorporating these practices into government climate action plans.
Regenerative Agriculture is a Unique Solution
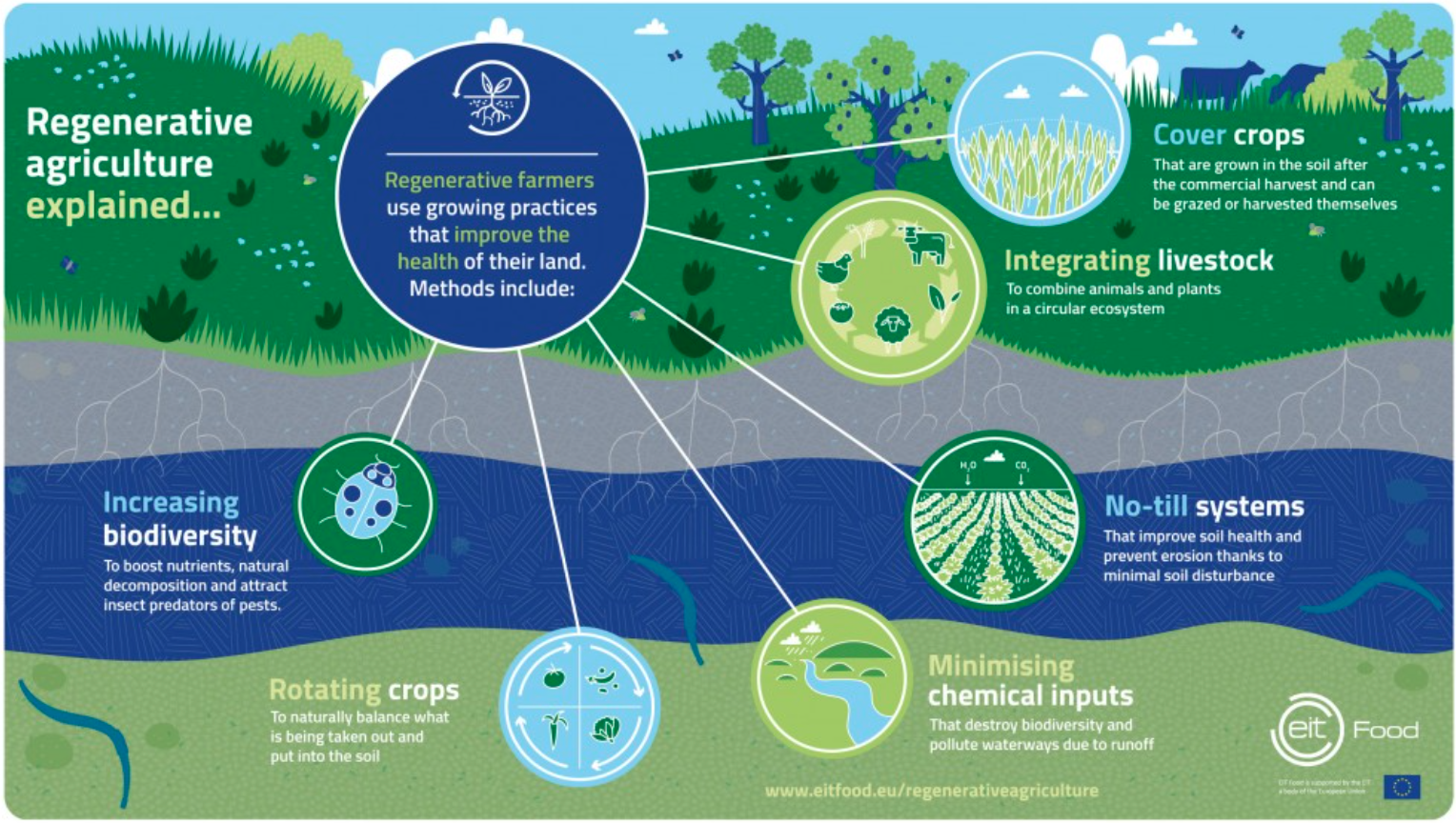
Regenerative agriculture represents a promising solution to climate change that has the potential to deliver a range of benefits for the environment, local communities, and the global food system. While there are significant challenges associated with scaling up and promoting these practices, there are also significant opportunities for growth and development. As consumer demand for sustainably-grown food continues to increase and climate policy solutions are developed, regenerative agriculture could play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of food production and helping to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Trending
-
1 How IoT is Revolutionizing Sustainability: A Brighter Future Beckons
Susanna Koelblin -
2 How The Water Treatment And Desalination Will Change The Environment For The Better
Daniel Hall -
3 How Intermediate Bulk Containers Enhance Environmental Sustainability
Daniel Hall -
4 Hybrid Cars and Their Key Benefits
Susanna Koelblin -
5 UK Faces Wettest July in Recent Memory
Daniel Hall





Comments