
AI Everywhere: Across the Edge & Sustainable
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) is ubiquitous, offering transformative opportunities across various industries.
One such paradigm shift is the convergence of AI with edge computing, facilitating sustainable solutions and innovative applications.
#IntelAmbassador #5thGenIntelXeon
Intel launched its 5th Gen. Xeon Scalable Processor on December 14th 2023, just immediately after the UN COP 28 summit closed with the announcement of a deal being agreed to transition towards a cleaner world. Technology will play a key role in our transition towards a cleaner economy and towards better ESG (Environment, Social and Governance) commitments.
Furthermore, the rapid advancement of AI has enabled companies to transform their services and operations with mass hyper-personalisation at scale in terms of customer experience (CX) and predictive analytics to manage business operations.
AI, 5G & IoT Convergence
The advantages provided by 5G networks are:
-
Low latency.
-
Massive increase in device connectivity in turn allowing scaled up machine to machine communications.
-
The emergence of AIoT across internet connected devices and sensors leading to mass hyper-personalisation at scale.

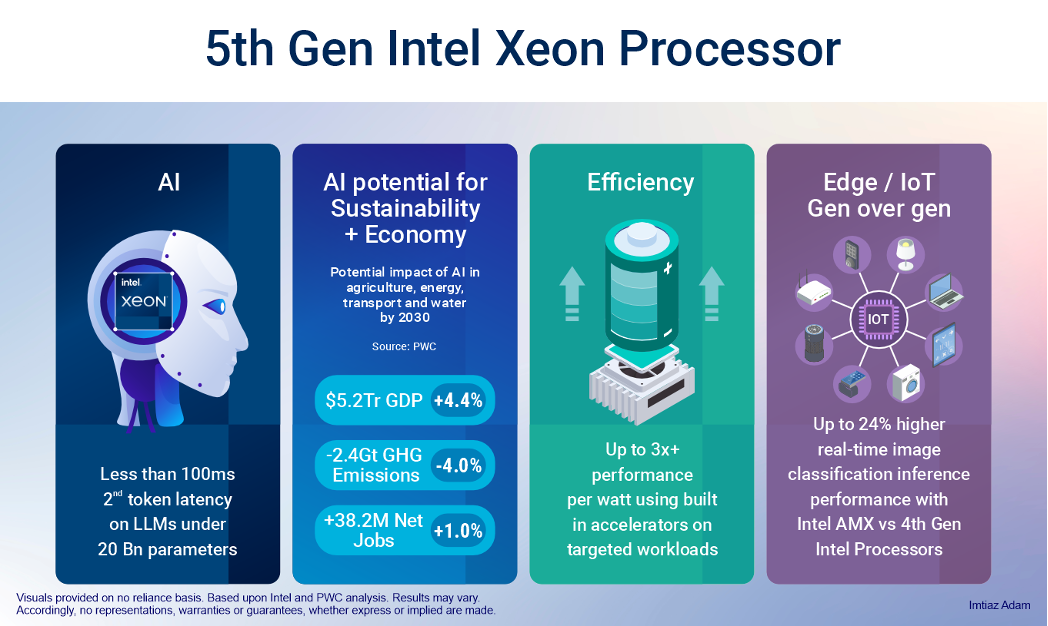
Environment & Economy
PWC issued a report, commissioned by Microsoft, that set out the potential of AI to help reduce carbon emissions.[1] An AI-enabled economy applied to the four sectors of agriculture, energy, transportation and water by 2030 may according to the analysis by PWC yield a gain of up to:
-
$5.2 Trillion or 4.4% of GDP towards global economic growth.
-
2.4Gigatonnes, or 4%, reduction in emissions of GreenHouse Gasses (GHGs).
-
Increase net jobs by 38.2 million or 1% globally.
The author believes that environmental and economic aims can be aligned, in particular, by advancing technology. More efficient AI is better at the macro-economic and social level to enable scaling and create economic and jobs growth, as companies and the overall economy grows. At a micro-economic level, by reducing the costs of deploying and scaling AI, companies may expand into new services, products and business models, and startups thrive and scale. At the same time, enabling this with lower energy consumption enables lower carbon footprints.
Furthermore, a group of leading AI research scientists laid out how Machine Learning could be deployed to assist in tackling climate change across electrical systems, industry, transportation, buildings, smart grids, disaster management and other sectors.[2] The challenge to secure such benefits is to enable AI to scale on an efficient basis including both costs and environmental (with energy efficiency being key to both aspects).

There has been a wave of excitement about the emergence of Generative AI that is typically enabled by Large Language Models (LLMs) that have adopted the Transformer with Self-Attention Mechanism architecture, often combined with Deep Reinforcement Learning approaches to reward the correct response. However, these models are computationally resource-expensive, including server requirements, energy costs and carbon footprint.
According to Intel, the 5th Gen. Xeon Scalable Processor with built-in accelerators, enables less than 100 milliseconds 2nd token latency on LLMs that are under 20 Billion parameters in size and up to 42 percent higher inferencing and fine-tuning on models as large as 20 Billion parameters, without the need for an additional accelerator thereby increasingly the accessibility and scalability of LLM models (based upon Intel’s internal modelling as of Dec 2023 see AI, A2, A16).
AI Everywhere: From Smart to a ‘Smart + Intelligent’ Edge
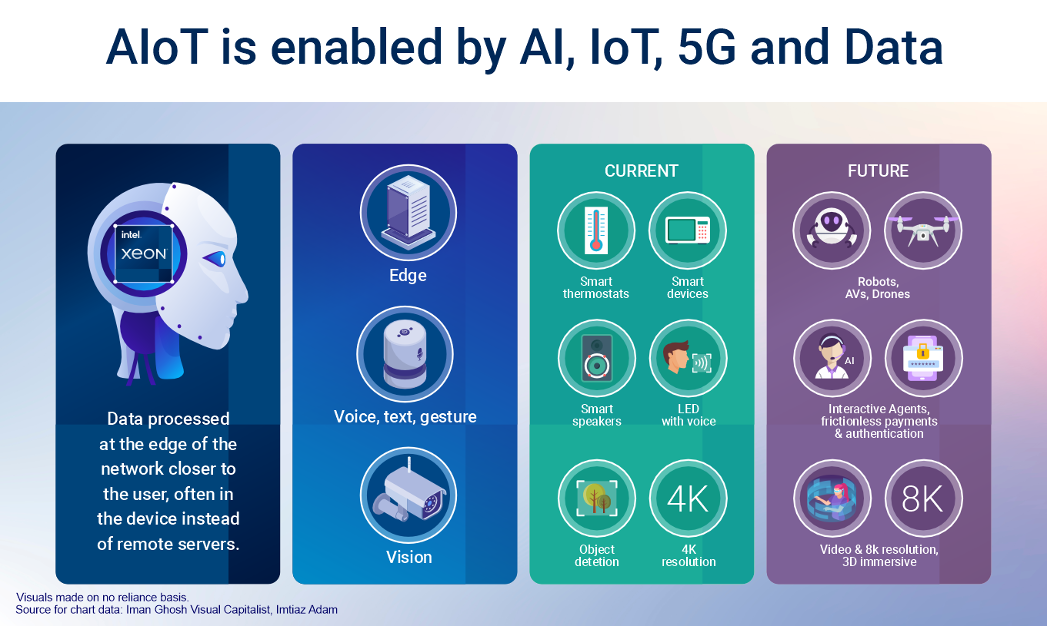
Smart refers to an internet connected device. However, connected devices are increasingly becoming ‘intelligent’ with AI embedded locally on the device (for example a PC with AI) with intelligence in this case, referring to the ability to respond meaningfully to the user and personalise the experience rather than human level intelligence.
The growth of edge computing as IoT scales, will require ultra-low latency, which in turn, allows for real-time responses.
As noted above, AI will increasingly be on the edge of the network (referred to as edge computing or simply the edge), whereby data is processed nearer to where it is generated and may actually be on the device itself. This allows for very low latency and hence real-time responses to the user.
Cloud / Edge Hybrid with Security & Reliability as Key Factors
The cloud model will continue with data centres, providing important resources and capacity to store historical data for analysis. This will also allow for ongoing algorithm development with a hybrid model, supporting training AI models on the cloud server and inferencing AI on the edge, that in turn providing further potential for mass personalisation at scale. The 5th Gen. Xeon Scalable Processor also allows for efficiency and reliable performance for the data centres that companies increasingly rely on for secure storage in the cloud.
For example, Intel® Software Guard Extensions (Intel® SGX) unlocks new opportunities for business collaboration and insights—even with sensitive or regulated data. SGX is the most researched, updated, and deployed confidential computing technology in data centres on the market today, with the smallest trust boundary. Confidential computing improves the isolation of sensitive data with enhanced hardware-based memory protections.
Examples of AI on the Edge
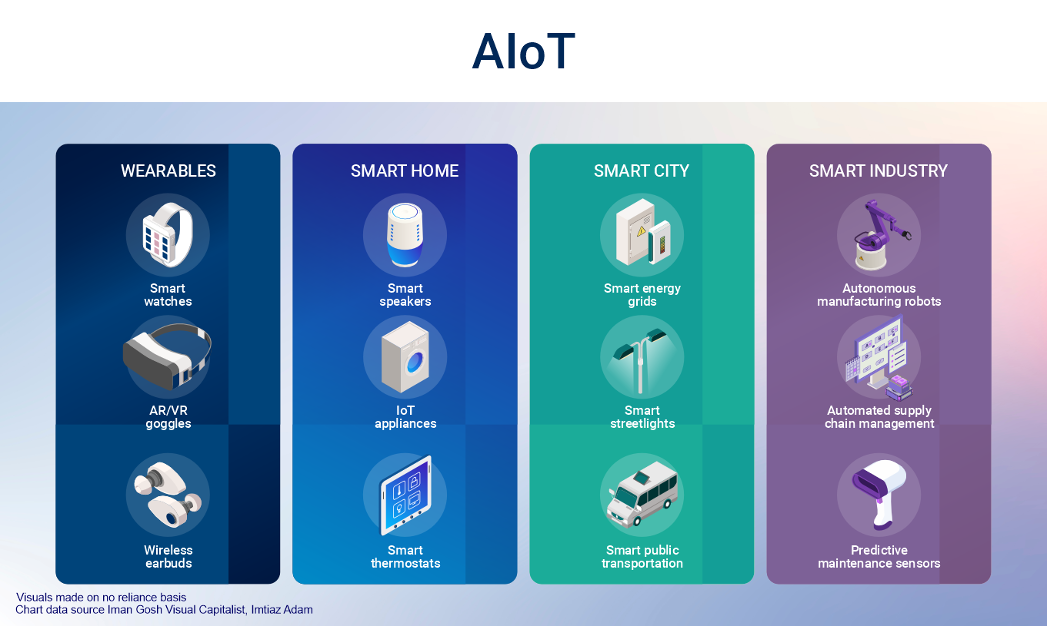
-
Smart grids that enable a real-time two-way flow of information and combining them with AI models such as NowCast and GraphCast from Google DeepMind to forecast weather and optimise renewable energy supply and demand management.
-
Microgrids enabled by IoT that may operate in grid-connected or detached-island setting and, enable locally produced energy, manage power outages and enhance efficiency gains.
-
Smart meters with embedded sensors to transmit real-time information and detect outages and quality of power supply monitoring.
-
Battery optimisation for renewable energy storage.
-
Drones with computer vision to inspect solar panels and wind turbines and detect damage which in turn may also reduce electricity generation.

-
Unplanned outage prediction and automated intervention.
-
Green hydrogen and fuel cell development.
-
Green AI for Automated Machine-Learning.
-
Urban traffic management planning for predicting traffic congestion and reroute traffic.
-
Algorithms that plan the journey of an EV so as to optimise between battery charge, distance and available charging points.

-
Researchers from Cambridge University have developed a Machine Learning algorithm that may reduce charging times and extend battery life in EVs by predicting how variations in patterns of driving may affect battery performance, improve reliability and safety.
-
AI has been deployed in the construction of intelligent, smart buildings where IoT sensors may detect the presence or absence of people in a room and adjust the heating/air conditioning or lighting accordingly so as to optimise energy consumption.
-
Applying Generative AI towards architecture and planning phase of buildings so as to predict potential issues with digital twins, and optimise the design for sustainability.
-
Manufacturing sector with predictive analytics applied towards unplanned outages and automation to reduce their occurrence so as to optimise production runs and reduce wastage that such outages may cause.
-
Optimisation of energy consumption and carbon footprint of manufacturing processes and supply chains.
-
Retail sector with recommendations applied alongside predictive analytics to enable brands to enhance demand forecasting and optimise their supply inventory and production.
5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable Processors and the Edge
According to Intel, the 5th Gen Xeon Scalable Processors provide substantial performance gains for AI on the Edge as set out below:
-
Gen-over-gen: up to 24% higher real-time image classification inference performance with Intel Advanced Matrix Extensions (Intel AMX), compared to 4th Gen Intel Xeon processors.[3]
-
3-year refresh
-
Up to 8x higher real-time image classification inference performance with AMX, compared to 3rd Gen Intel Xeon processors with FP32. [4]
Examples Provided by Intel: Media, Video and Retail
Media: Super resolution (image & video upscaling) 4k video upscale with the power of AI
- Help ensure that lower-resolution video content can fit onto 4k screens and monitors without losing quality. 5th Gen Xeon Scalable processors feature built-in AI acceleration with AMX, making it fast and easy to upscale video to 4K. This is ideal for studios, broadcasters, and telecommunications providers. Intel AI and OpenVINO software tools make it easier for developers to leverage new processor capabilities, like Intel AMX.
Video edge server
-
Drive productivity and efficiency with video analytics.
-
Use video to enhance your operations, marketing, and customer experiences. Extract insights and metadata—such as scene changes, objects, faces, speech, and more—with video structurization servers powered by 5th Gen Xeon Scalable processors.
-
With AMX, you can accelerate inference and analytics at the edge. Intel AI and OpenVINO software tools powered by oneAPI make it easier for developers to leverage new processor capabilities, like Intel AMX/TMUL for BF16.
Retail: Automated check-out
-
Smarter retail, better experiences.
-
Create more enjoyable—and profitable—retail experiences with AI at the edge. With 5th Gen Xeon Scalable processors, you can implement video analytics in a wide range of retail and hospitality environments.
-
Quickly and efficiently analyse video data with AMX, to extract valuable insights about objects, customers, inventory, and more. The results can deliver faster insights on customer behaviour and storefront utilization, inform product and service positioning to customers, and help optimize product and service revenue, staff productivity, and environment safety.
-
Scale up to support larger deployments with higher core counts, multiple sockets, and up to 80 lanes of PCIe 5.0 that make it possible to add GPUs, FPGAs, or other peripherals.
Enhanced Sustainability (from Intel)
-
5th Gen Xeon Scalable processors are Intel’s most sustainable data centre processors ever. Lower one’s carbon footprint—and one’s TCO—with built-in accelerators to improve performance per watt and features for managing power efficiency.
-
The latest Intel Accelerator Engines help improve power efficiency across AI, data analytics, networking, and storage workloads. A built-in accelerator can often deliver the highest level of performance for a workload with better results than simply using more general-purpose cores.
-
Up to 10x higher performance per watt using built-in accelerators on targeted workloads.[5]
-
Up to 3x higher performance per watt with built-in accelerators vs. 4th Gen AMD EPYC processors.[6]
-
Make dynamic adjustments to save electricity as computing needs fluctuate. Intel Xeon processors have built-in telemetry tools, like Intel Data Centre Manager (Intel DCM), to help monitor and manage CPU resources.
-
With Intel’s Granulate, one may improve performance and energy efficiency and reduce costs by up to 45% with no code changes or R&D efforts by optimizing OS and runtime resource management.[7]
Governance: Security, Reliability, Quality
From the governance perspective in terms of security and quality the 5th Gen Xeon Scalable Processors are designed to enhance the data security and quality aspects due to the following:
-
Software- and pin-compatible with 4th Gen Intel Xeon processors.
-
Silicon-based security features, confidential computing, and trust services.
-
Leading quality and enhanced telemetry.
-
Largest ecosystem of hardware and software vendors.
For further reference see also:
Intel® Software Guard Extensions (Intel® SGX) – Confidential computing web page
Intel® Trust Domain Extensions (Intel® TDX) – Confidential computing web page
Intel® Virtual RAID on CPU (Intel® VROC) – Intel VROC web page
Summary
In summary the 5th Generation of Intel Xeon Scalable Processors are designed to enable the world of AI everywhere providing for the AIoT to effectively scale on a more efficient, sustainable basis and providing for reliable, robust standards for security and quality.
All performance data provided by Intel. Results may vary and are provided on a non-reliance basis and although the author has made reasonable efforts to research the information, the author makes no representations, warranties or guarantees, whether express or implied is provided in relation to the content in this article. up-to-date
[1] PWC How AI can enable a Sustainable Future Commissioned by Microsoft.
[2] Rolnick et al. Tackling Machine Learning with Climate Change (2019) with Andrew Y Ng, Yoshua Bengio and Demis Hasibis as fellow authors.
[3] As measured by performance on ResNet50v1.5. See A26 at intel.com/processorclaims: 5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors. Results may vary.
[4] As measured by performance on ResNet50v1.5. See A26 at intel.com/processorclaims: 5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors. Results may vary.
[5] Based on performance per watt gains of 1.46x to 10.6x with built-in accelerators on a range of AI, database, and networking workloads. See A19-A25, D1, D2, D5, N16 at intel.com/processorclaims: 5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors. Results may vary.
[6] Based on performance per watt gains of 1.11x to 2.96x with built-in accelerators on a range of AI, database, networking, and HPC workloads compared to AMD EYPC 9554, 9654, and 9754. See A208-A211 D201-D204, H201, N201 at intel.com/processorclaims: 5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors. Results may vary.
[7] Source: : https://granulate.io/solutions/intel/.
Trending
-
1 How Does SaaS Differ From IaaS And PaaS?
Fabrice Beaux -
2 Single Page Applications vs Multi-Page Applications
Fabrice Beaux -
3 Top 7 Effective Strategies for Multi-Language Website Development
Fabrice Beaux -
4 Boost Engagement to Infinity and Beyond: Unleashing AI-Driven Support
Anas Bouargane -
5 The Cheapest And Most Beautiful Stickers in CS2
Daniel Hall





Comments