
The Evolution of Blockchain
Bitcoin and the first blockchain innovation came into existence for over a decade. They were created with the idea of providing an easier platform to transfer value between two parties, without the need of a third-party. Blockchain has been a revolutionary innovation ever since its inception widely used across multiple industries.
Throughout the last decade, it has been developed further and has been applied in various applications and products. It is independent of country borders and national currencies. This is the reason why it is seen as the greatest innovation since the Internet.
Over the years, new blockchain applications have grown over industries. Bitcoin is one of the first beneficiaries of the blockchain revolution before the emergence of second and third generation blockchain platforms. In this article, we will explore all three generations of blockchain.
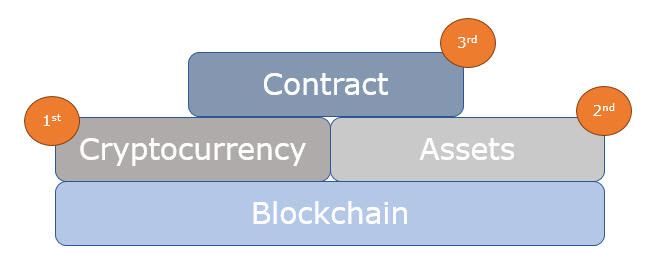
1st Generation – Cryptocurrencies
The first major blockchain application was Bitcoin, the most renowned digital currency. For the first time, it was possible to transfer money without any third-party intervention. Each bitcoin transfers the complete ownership and record of transactions. This type of money is termed as a cryptocurrency. The founder of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto, made the code behind Bitcoin an open source, gaving everyone the opportunity to learn, build and expand beyond it.
2nd Generation – Assets
The second generation of Blockchain includes the likes of Ethereum, NEO and QTUM which help in recording transactions that happen over a blockchain network and also expands it to involve programming language.
As the bitcoin became a hype in the tech world, it brought in new ideas to apply the blockchain ledger to broader use cases, by offering the administration of assets. Individuals were allowed to issue shares on Blockchain. The shares could receive dividends and the shareowners could also get the voting rights. This idea facilitated the idea of crowd ownership that fits well in the generation that promotes crowdfunding and sharing economy.
3rd Generation – Smart Contracts, Proof of Stake and Blockchain Scaling
Blockchain also had the capability to register agreements. Smart Contracts are basically computer programs that are fed into the blockchain network which allowed financial instruments like loans or bonds to be also represented instead of only cash-like tokens like the bitcoin. A smart contract enforces the participant to keep their promise. For example, imagine an insurance contract that requires payments at regular intervals. If the payee fails to make the payment, the contract ends. Smart Contracts are a very useful technology to automate processes in the future.
There were blockchain networks that were secured by ‘proof of work’ where the group, called miners, with the largest total computing power gets the right of making the decisions. These miners operate data centers to provide security for the cryptocurrency payments. The proof of stake concept states that a person can mine and validate a transaction depending upon the number of coins he holds in his wallet. The higher the bitcoin, the higher the power to control the transaction.
It was the third generation where the idea of blockchain scaling came into place. Currently, every computer in the network processes every transaction making the system slow. A scaled blockchain accelerates the process by analyzing how many computers are actually important to process the transaction, without compromising on the security and robustness of the system.
What’s Next?
New concepts such as Soferox – Proof of Pact have emerged to reap maximum benefits out of this technology. There is also Graphene that helps the processing done by nodes in a more effective activity. As the network continues to grow, it will be interesting to look at the new ideas that will lead the way to a faster and more reliable transactional environment.
Trending
-
1 How Does SaaS Differ From IaaS And PaaS?
Fabrice Beaux -
2 Single Page Applications vs Multi-Page Applications
Fabrice Beaux -
3 Top 7 Effective Strategies for Multi-Language Website Development
Fabrice Beaux -
4 Boost Engagement to Infinity and Beyond: Unleashing AI-Driven Support
Anas Bouargane -
5 The Cheapest And Most Beautiful Stickers in CS2
Daniel Hall





Comments