
The Future of Applied AI: Towards A Hyperpersonalised & Sustainable World
Business leaders are facing the challenges of addressing sustainability goals including reducing carbon footprint and managing energy consumption costs, whilst also ensuring that they position their firm to take advantage of the rapid pace of change and new business opportunities that advancing technology, in particular AI, is enabling across every sector of the economy.
As an Intel Ambassador, I am delighted to continue my collaboration with Intel in relation to the 4th Generation of Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors and the potential to scale AI across the economy whilst also helping meet sustainability objectives.
With built-in accelerators and software optimizations, 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® with built-in Accelerators have been shown to deliver leading performance per watt on targeted real-world workloads. This results in more efficient CPU utilization, lower electricity consumption, and higher ROI, while helping businesses achieve their sustainability goals.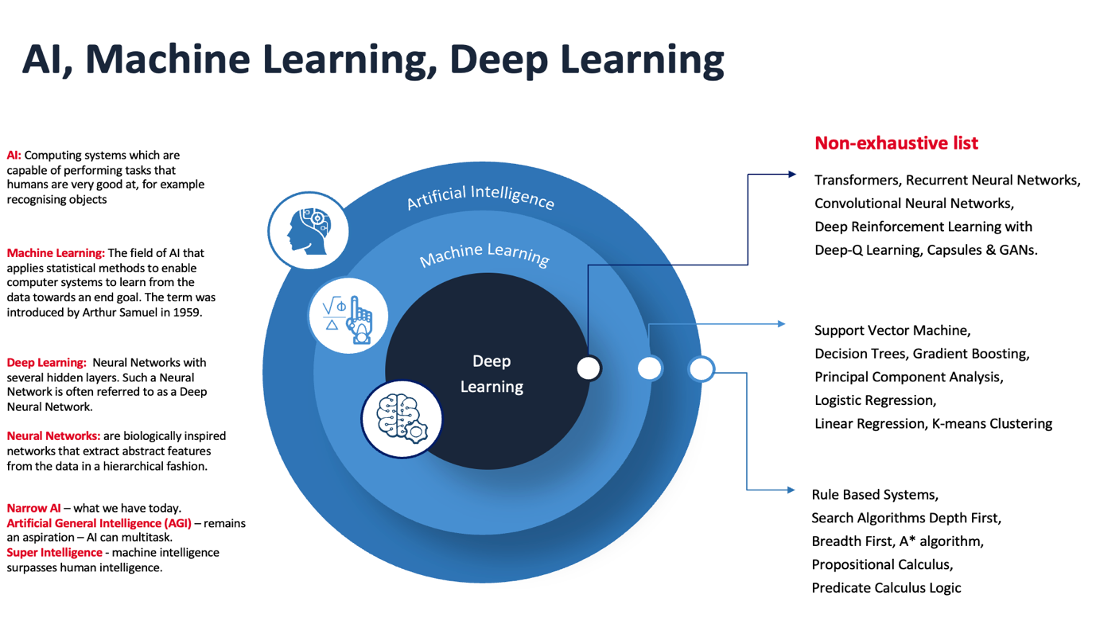
One may add broad AI or Artificial Broad Intelligence (ABI) into the categories on the lower left side from the image above. We are now in the era of ABI as Multimodal, Multitasking Transformers from the likes of Microsoft, Google, OpenAI, and others enable certain Deep Learning algorithms to perform both vision and natural language processing (NLP) tasks, albeit such powerful algorithms require capable Central Processing Units (CPUs) and Graphical Processing Units (GPUs) that scale to perform well.
Intel® 4th Generation Xeon® Scalable Processors enable accelerated AI workloads 3x to 5x for Deep Learning inference on SSD- ResNet34 and up to 2x for training on ResNet50 v1.5 with Intel® Advanced Matrix Extensions (Intel® AMX) compared with the previous generation. Furthermore, in terms of AI performance the 4th Gen Intel®Xeon® Scalable Processors deliver up to 10X higher PyTorch performance for both real-time inference and training with built-in AMX (BF16) vs prior generation. (FP32).
As we enter an era of ever more powerful AI algorithms such as Transformers with Self-Attention and Generative AI and the rise of AI meets the IoT (AIoT) we’ll need the kind of capability that the 4th Generation Gen Intel®Xeon® Scalable Processors deliver with more efficient and powerful CPUs that allow for AI to scale and process large volumes of data very rapidly in low latency use cases, and yet at the same time to do so with energy efficiency and reduced carbon footprint as a key objective too.
How May AI Help with Sustainability & the battle against Climate Change?
Microsoft commissioned a report from PWC entitled “How AI can deliver a sustainable future” in relation to the potential for AI across four sectors of the global economy:
-
Energy;
-
Agriculture;
-
Water;
-
Transportation.
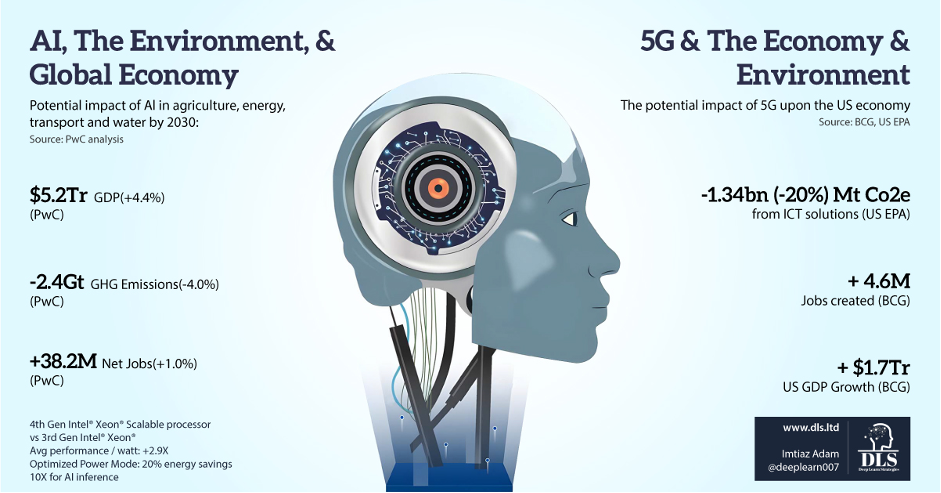
The results from the report demonstrated the potential of AI to drive a reduction in emissions, whilst also increase jobs and economic growth across the four sectors explored in the report:
-
Reduction of CO2 emissions by up to 4% globally;
-
GPD growth of 4.4% amounting to a vast $5.2 trillion;
-
Employment growth amounting to a net 38 million jobs created.
The potential for the reduction in GHG emissions (up to 4% globally) is based upon assumptions applied across all four sectors (water, energy, agriculture and transportation) and the role that AI may play across those sectors including but not limited to precision agriculture, precision monitoring, fuel efficiencies, optimising use of inputs, higher productivity.
Furthermore, the resulting gains from Standalone 5G networks was set out by the US EPA and BCG (see right side of infographic above) whereby the resulting ability of SA 5G networks to enable massive scaling of the AIoT (AI applied onto IoT devices and sensors) and the increased automation flows with machine-to-machine communications may result in both a jobs gain and potential to reduce GHG emissions.
The latest Intel® Accelerator Engines and software optimizations help improve power efficiency across AI, data analytics, networking and storage. Organizations can achieve a 2.9x average performance per watt efficiency improvement for targeted workloads utilizing built-in accelerators compared with the previous generation. This leads to more efficient
CPU utilization, lower electricity consumption and higher return on investment, while helping businesses achieve their sustainability and carbon reduction goals.
Enabling Change
The 4th Generation of Intel®Xeon® Scalable Processors provide energy efficiency improvements achieved due to innovations within the design of the built-in accelerators. This allows for particular workloads to consume less energy whilst running at faster speeds.
The result per watt (on average) is 2.9X over the 3rd Gen Intel Xeon Processors whilst also allowing for massive scaling of workloads that will needed in the new era of the AIoT that we are entering into, for example inferencing and learning increased by 10X, 2X for improved compression, 3X for data analytics all achieved with 95% less cores. [1]
Another innovation is the Optimized Power Mode feature that, when enabled, provides 20% energy savings (up to 140 Watts on a dual socket system) while only minimally impacting performance (2-5% on select workloads).
The convergence of Standalone (SA) 5G Networks that will allow for a massive increase in device connectivity and ultra-low latency environments will allow for a massive scaling of the Internet of Things (IoT) with internet connected devices and sensors communicating with human users and each other (machine to machine). Increasingly these IoT devices will have AI embedded onto them (on the edge of the network).
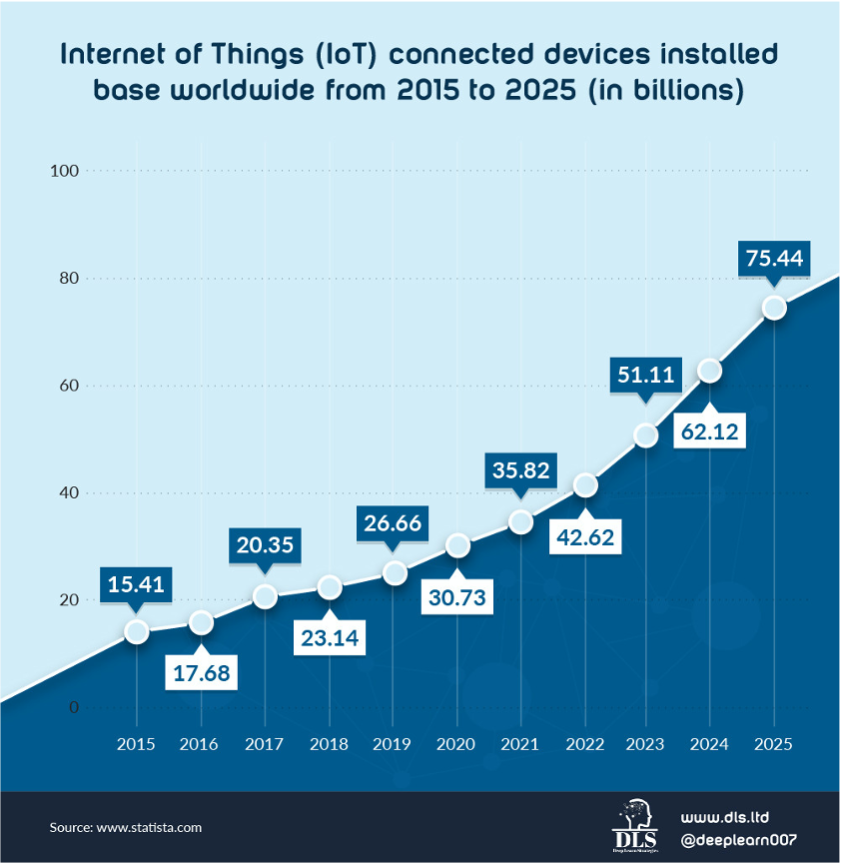
Furthermore, Statista forecast that by 2025 there will be a staggering 75 billion internet connected devices, or over 9 per person on the planet! And IDC Seagate forecast that the volume of data generated will increase from 64 Zetabytes in 2020 (when we talked about the era of big data) to almost three times the volume amounting to 175 Zetabytes in 2025 with 1/3rd of this data consumed in real-time! Applying AI will be essential to efficiently manage networks and also to make sense of the data and provide near real-time responses to users.
Furthermore, this new era will allow us to measure, analyse (evaluate) and respond dynamically to our environment (whether that be healthcare, energy, smart cities with traffic, manufacturing, etc). AI capabilities and inference performance will be key to succeed in this era that we are entering into.
A world where Machine-to-Machine Communication reduces risk (broken down car is detected by the red car that then broadcasts to other vehicles around it who also then broadcast and thereby also avoid traffic jams where emissions can increase due to slow moving traffic) as shown in the illustration below.
Intel®Xeon® Scalable processors provide for more networking compute at lower latency while helping preserve data integrity. Achieve up to 79% higher storage I/O per second (IOPS) with as much as 45% lower latency when using NVMe over TCP, accelerating CRC32C error checking with Intel® Data Streaming Accelerator (Intel® DSA), compared to software error checking without acceleration.
BCG in an article entitled “Reduce Carbon and Costs with the Power of AI“ forecast that AI technology applied towards corporate sustainability goals may yield reductions of 2.6 to 5.3 gigatons or 1 to 3 USD trillion in value added.
The process for achieving this entails:
-
Monitoring emissions;
-
Predicting emissions;
-
Reducing emissions.
BCG believes that the sectors with the greatest potential for reductions of GHGs due to application of AI include: Industrial goods, transportation, pharmaceutical, consumer packaged goods, energy and utilities.
Intel’s vision is to accelerate sustainable computing, from manufacturing to products to solutions, for a sustainable future. Organizations can help reduce their scope 3 GHG emissions by choosing 4th Gen Gen Intel®Xeon® Scalable Processors, which are manufactured with 90-100% renewable energy at sites with state-of-the-art water reclamation facilities that in 2021 recycled 2.8 billion gallons of water. For the avoidance of doubt, it is noted that the statistics provided in this paragraph entail Scope 3 emissions related to embodied carbon that don't impact the operational emissions of carbon, however, Scope 3 also includes operational carbon within which servers form a larger part of the equation.
Use case examples of applying the AIoT towards sustainability include the following:
-
Sensors that may detect that a no person is present in a room and hence switch off the lights and turn the heating (or if summer the air conditioning) off or to a lower level;
-
Sensors that may realise that a window is open whilst the heating is running and close it;
-
Predicting issues before they occur such as bust water pipes, unplanned outages in monitoring, traffic congestion spots and trying to reroute traffic or amend the traffic light sequencing to reduce the jams;
-
In relation to agriculture applying computer vision on a drone to determine when the crops are ripe for harvesting (so as to reduce wasted crops) and also to check for signs of drought and insect infestations;
-
Deforestation – near real-time analytics of illegal logging.
-
Renewable energy – drones applying Computer Vision from Deep Learning algorithms that may inspect the blades of wind turbines and solar panels on solar farms for cracks and damages thereby improving asset life and enhancing amount generated.
-
Energy storage optimisation with Machine Learning algorithms applied towards maximising the operational performance and return on investment for battery storage.
Rolnick et al. (2019) published a paper entitled “Tackling Climate Change with Machine Learning” (co-authored by leading AI researchers including Demis Hassabis (Co-founder of DeepMind), Andrew Y Ng, and Yoshua Bengio set out the potential to reduce emissions by applying AI across the manufacturing operations of a firm all the way from the design stage with generative design and 3D printing, supply chain optimization with a preference for low greenhouse gas emissions options, improving factory energy consumption with renewable supplies and efficiency gains (including predictive maintenance) through to detection emissions with the follow up action of abating emissions from heating and cooling and optimizing transport routes.
The 4th Generation of Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors also have power management tools to enable more control and greater operational savings. For example, new Optimized Power Mode in the platform BIOS can deliver up to 20% socket power savings with a less than 5% performance impact for selected workloads.
Furthermore, the paper by Rolnick et al. sets out how firms may deal with the unsold inventory problem for retailers with some estimates placing the annual costing the fashion industry $120 billion a year! This is both an economic and an environmental wastage. Targeted recommendation algorithms to match supply with demand, and application for Machine Learning towards forecasting demand and production needs may also help reduce such wastage.
In the world of the AIoT a customer could be walking along the high street or the mall and a Machine Learning algorithm could offer them personalised product recommendations based upon the stores in close proximity to them.
Both the retail and manufacturing examples would require near real-time responses from the AI algorithms and hence a reason why accelerators within the CPU are important factors to deliver enhanced performance.
The world of the AIoT will require the ability to work within power constrained environments and respond to user needs in near-real time.
Intel enables organizations can make dynamic adjustments to save electricity as computing needs fluctuate. Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors have built-in telemetry tools that provide vital data and AI capabilities to help intelligently monitor and manage CPU resources, build models that help predict peak loads on the data centre or network, and tune CPU frequencies to reduce electricity use when demand is lower. This opens the door to greater electricity savings, the ability to selectively increase workloads when renewable energy sources are available and an opportunity to lower the carbon footprint of data centres.
In addition, only Intel offers processor SKUs optimized for liquid-cooled systems, with an immersion cooling warranty rider available, helping organizations further advance their sustainability goals.
AI will literally be all around us across the devices and sensors that we use, allowing for mass hyper- personalisation at scale with near real-time instant responses to the customer user. However, in order to avail these opportunities business leaders will need to ensure that they have invested in the appropriate technology that can meet the needs of the business and its customers.
We are entering an era where near immediate responses (often on the fly) will be necessary to engage with customers and also to respond dynamically in a world of machine-to-machine communication.
Intel® Advanced Matrix Extensions (Intel® AMX) allows for efficient scaling of AI capabilities to respond to the needs of the user and the network.
Significantly accelerate AI capabilities on the CPU with Intel® Advanced Matrix Extensions (Intel® AMX). Intel AMX is a built-in accelerator that improves the performance of Deep Learning training and inference on 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors, ideal for work-loads like natural language processing, recommendation systems, and image recognition.
4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors have the most built-in accelerators of any CPU on the market to deliver performance and power efficiency advantages across the fastest growing workload types in AI, analytics, networking, storage, and HPC. With all new accelerated matrix multiply operations, 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors have exceptional AI training and inference performance.
Other seamlessly integrated accelerators speed up data movement and compression for faster networking, boost query throughput for more responsive analytics, and offload scheduling and queue management to dynamically balance loads across multiple cores. To enable new built in accelerator features, Intel supports the ecosystem with OS level software, libraries, and APIs.
Performance gains from the 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors include the following (source 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors perf index):
-
Run cloud and networking workloads using fewer cores with faster cryptography. Increase client density by up to 4.35x on an open-source NGINX web server with Intel® QuickAssist Technology (Intel® QAT) using RSA4K compared to software running on CPU cores without acceleration.
-
Improve database and analytics performance with 1.91x higher throughput for data decompression in the open source RocksDB engine, using Intel® In Memory Analytics Accelerator (Intel® IAA) compared to software compression on cores without acceleration solutions with 8.9x increased memory to memory transfer using Intel® Data Streaming Accelerator (Intel® DSA), versus previous generation direct memory access.
-
For 5G vRAN deployments, increase network capacity up to 2x with new instruction set acceleration compared to the previous generation.
Security is a key issue in the era of the AIoT as SA 5G networks expand and scale.
Businesses need to protect data and remain compliant with privacy regulations whether deploying on premises, at the edge, or in the cloud. 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors unlock new opportunities for business collaboration and insights even with sensitive or regulated data. Confidential computing offers a solution to help protect data in use with hardware-based isolation and remote attestation of workloads. Intel® Software Guard Extensions (Intel® SGX) is the most researched, updated, and deployed confidential computing technology in data centres on the market today, with the smallest trust boundary of any confidential computing technology in the data centre today. Developers can run sensitive data operations inside enclaves to help increase application security and protect data confidentiality.
Intel’s Bosch case study provides an example of an application of security in the IoT sector.
The case study observed that access to raw data sets is ideal for the development of analytics based on Artificial Intelligence. The example sets out how Bosch’s autonomous vehicles unit reduced risks associated with data or IP leakage using the open source project Gramine, running on Intel SGX. For more details, please refer to Implementing Advanced Security for AI and Analytics.
By the end of this decade, we may experience a substantial increase in the number of advanced Electric and Autonomous Vehicles (EVs and AVs) on the road and a world where
battery storage will be of greater importance as more renewable energy scales across the grid (following the Inflation Reduction Act in the US, and the continued policies of the UK and EU towards reducing carbon emission targets). Powerful CPUs with built in accelerators can help Machine Learning techniques scale across battery storage facilities to optimise the availability of energy and battery performance. This is relevant for edge and network scenarios with power and battery constraints, such as EVs and power-optimized devices in smart homes and manufacturing facilities.
In this world mass hyper-personalisation at scale enabled by the AIoT will allow for both near real-time engagement with the customer on the fly as well as greater efficiency and hence less wastage as Machine Learning and Data Science will enable superior prediction of customer needs from the vast amount of data that will be created.
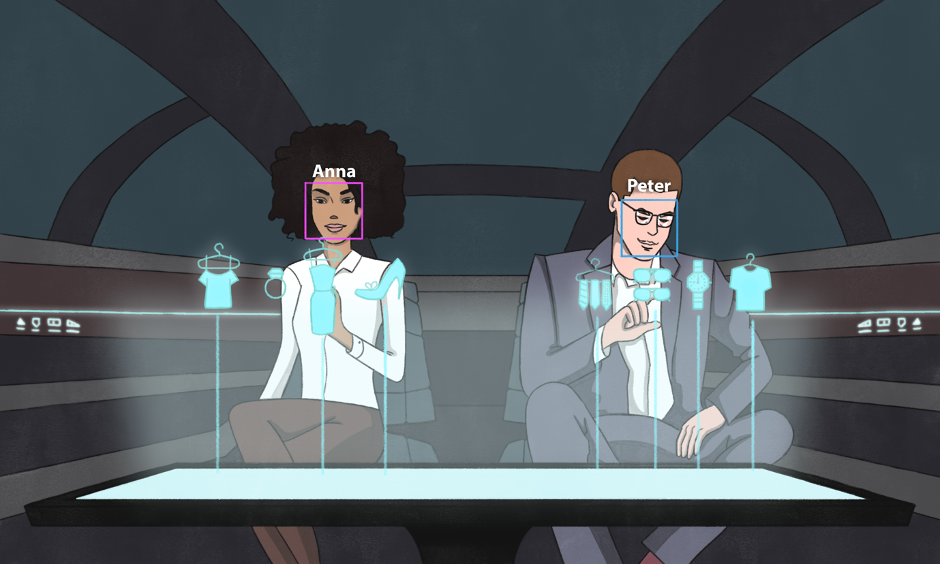

One may imagine the users engaging in retail or entertainment on their way into and back home from work and the EV/AV recognising the passengers with Computer Vision from Deep Learning and personalising the environment of the car (entertainment, etc) to the user profile. The AV/EVs will go on one journey to another adjusting to different passengers and allowing the user to utilize their time efficiently and as they wish (engaging with brands, working, entertainment). However, even before more advanced EV/AVs arrive, there are many opportunities for firms to avail in the era of the AIoT for near real-time engagement with the customer whilst also reducing wastage (for example better matching supply and demand, improved demand forecasting, identifying and matching supply chain and manufacturing processes).
The 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors enable a more secure environment for developing IoT services and applications across the edge of the network, in turn enabling businesses to create new opportunities with greater confidence around security.
This vision of scaling and enabling a secure AIoT aligns with my own personal vision of applying AI and related data analytical and digital technology to deliver on sustainability objectives whilst also delivering world of genuine mass hyper-personalisation at scale whereby firms can truly respond to their customer’s needs in real-time conditions and further tailor their offerings to the individual customer’s needs.
We’re entering an exciting new era from this year and across the rest of this decade whereby AI will scale rapidly across the devices and sensors around us as well as the remote cloud servers that will continue to remain important for training algorithms, acting as data lakes and enabling analytics on historic data to improve learning outcomes for AI and improve the personalisation of service or identify the opportunities to further enhance operational efficiencies across organisations.
We’ll be able to measure and evaluate emissions and energy consumption around us and identify wastage and reduce inefficiencies.
The AI algorithms across the Edge of the network will require energy efficient CPUs to operate across power constrained environments and to achieve reduced carbon footprint. The 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors allow organisations to scale AI capabilities, provide hyper-personalisation at scale, and manage their internal operations at the Edge more efficiently whilst also helping enable security and sustainability goals to be met.
Imtiaz Adam
Data Scientist
Postgraduate in Computer Science with research in AI, Sloan Fellow
Trending
-
1 How Does SaaS Differ From IaaS And PaaS?
Fabrice Beaux -
2 Single Page Applications vs Multi-Page Applications
Fabrice Beaux -
3 Top 7 Effective Strategies for Multi-Language Website Development
Fabrice Beaux -
4 Boost Engagement to Infinity and Beyond: Unleashing AI-Driven Support
Anas Bouargane -
5 The Cheapest And Most Beautiful Stickers in CS2
Daniel Hall





Comments